Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Doda, Norihiro; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Hamase, Erina; Yokoyama, Kenji; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on State-of-the-art Thermal Hydraulics of Fast Reactors (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/09
ARKADIA-Design is being developed to support the optimization of sodium-cooled fast reactors in the conceptual design stage. Design optimization requires various types of numerical analysis: 1-D plant dynamics analysis for efficient evaluation of various design options and multi-dimensional analysis for a detailed evaluation of local phenomena, including multi-physics. For those analyses, ARKADIA-Design performs whole plant analyses based on the multi-level simulation (MLS) technique in which the analysis codes are coupled to simulate the phenomena in an intended degree of resolution. This paper describes an outline of the coupling analysis methods in the MLS of the ARKADIA-Design and the numerical simulations of the experimental fast breeder reactor EBR-II tests by the coupled analysis.
Doda, Norihiro; Hamase, Erina; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/04
In conventional design studies of sodium-cooled fast reactors, plant dynamics and local phenomena were evaluated separately by using simple models and detailed models, respectively, and their interaction was considered through the boundary conditions settings with conservativeness for each individual analysis. Thus, the final result through the analyses may contain excessive conservativeness. Therefore, JAEA began to develop a multi-level simulation system in which detailed analysis codes are coupled with a plant dynamics analysis code. Focusing on core thermal-hydraulics, a coupled analysis method using a plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD and a subchannel analysis code ASFRE has been developed. The analysis on a test in the experimental fast reactor EBR-II was performed to validate the coupled analysis. Through the comparison of the analysis results and the measurement, it was confirmed that the coupled analysis could predict the transient temperature distribution in the subassembly, and the multi-level simulation by changing the level of detail in analysis model could be performed for core thermal-hydraulics.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
For design optimization of fast reactors, in order to consider the feedback reactivity due to thermal deformation of the core when the core temperature rises, which could not be considered in the conventional design analysis, a neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structure mechanics coupled analysis method has been developed. Neutronics code, plant dynamics code, and structural mechanics code are coupled by a control module in python script. This paper outlines the coupling method of analysis codes and the results of its application to an experiment in an actual plant.
Doda, Norihiro; Hamase, Erina; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 25, 4 Pages, 2020/06
With the aim of advancing the design optimization in fast reactors, neutronics and thermal-hydraulics coupled analysis method which can consider the temporal change of neutron flux distribution in the core has been developed. A three-dimensional neutronics analysis code and a plant dynamics analysis code are coupled on a platform using Python programing. In this report, outlines of the coupling method of analysis codes, the results of its application to the actual plant under a virtual accidental condition, and the future development is described.
 secondary system and turbomachinery
secondary system and turbomachineryHumrickhouse, P. W.*; Sato, Hiroyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Sumita, Junya; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2018/10
This work describes the development of a RELAP5-3D model of the HTTR-GT/H plant secondary system. The RELAP5-3D model presently includes detailed models of several of the heat exchangers in the secondary system as well as the turbomachinery, which includes two compressors and two gas turbines connected to a common shaft and motor. The predictions of the model agreed well to design parameters in both sole power generation and hydrogen co-generation modes in most instances. Both the turbomachinery and heat exchanger models rely on extensive customization via RELAP5-3D control variables, and these implementations are outlined in detail. Potential improvements to the RELAP5-3D turbine model are discussed.
plant secondary system. The RELAP5-3D model presently includes detailed models of several of the heat exchangers in the secondary system as well as the turbomachinery, which includes two compressors and two gas turbines connected to a common shaft and motor. The predictions of the model agreed well to design parameters in both sole power generation and hydrogen co-generation modes in most instances. Both the turbomachinery and heat exchanger models rely on extensive customization via RELAP5-3D control variables, and these implementations are outlined in detail. Potential improvements to the RELAP5-3D turbine model are discussed.
Hamase, Erina; Doda, Norihiro; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Ono, Ayako; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 83(848), p.16-00431_1 - 16-00431_11, 2017/04
A plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD is being developed in JAEA for the design and safety assessments of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). In this study, the friction loss coefficients in the whole core thermal-hydraulic model was modified to improve the prediction accuracy of the sodium temperature distribution in a fuel subassembly under the natural circulation conditions. The modified whole core model was applied to analyses of experiments that were performed by using JAEA's test facility PLANDTL as a part of the code validation study. The obtained numerical results of sodium temperature distributions in the core showed good agreement with the measured data. It implies that the modified whole core model can properly reproduce dominant thermal-hydraulic phenomena in the core region under natural circulation conditions, i.e., flow redistribution among fuel subassemblies as well as in a fuel subassembly and inter-subassembly heat transfer.
Takata, Takashi; Azuma, Emiko*
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
A new approach has been developed to assess event sequences under external hazard considering a plant status quantitatively and stochastically so as to take various scenarios into account automatically by applying a Continuous Markov Chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) method coupled with a plant dynamics analysis. In the paper, a tornado and a strong wind are selected as the external hazard to assess the plant safety in a loop type sodium cooled fast reactor (SFR). As a result, it is demonstrated that the various scenarios where the order of the occurrence event and its occurrence time differs from each other can be assessed simultaneously as well as the statistical characteristics of plant parameter such as the coolant temperature. Furthermore, a weight factor is introduced so as to investigate the low failure probability events with a comparative small number of the sampling.
Kitano, Akihiro; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(7), p.992 - 1008, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)A feedback reactivity measurement technique was developed based on a reactivity model featuring components that depend on the reactivity coefficients, denoted as reactor power (K ) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K
) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K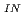 ). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K
). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K
showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K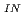 was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2
was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2 C.
C.
Onoe, Hironori; Kosaka, Hiroshi*; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu
JAEA-Research 2015-008, 146 Pages, 2015/08
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is being carried out by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the Cretaceous Toki granite in the Tono area, central Japan. The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation (Phase I), Construction (Phase II) and Operation (Phase III). In this study, calibration of hydrogeological model and groundwater flow simulation using the data obtained by the Phase I and Phase II were carried out in order to develop the methodology for construction and update of hydrogeological model on Site Scale. As a result, hydrogeological model on Site Scale, which is able to simulate comprehensively the obtained data regarding groundwater pressure distribution before excavation of the MIU facilities, hydraulic responses and inflow volume during excavation of the MIU facilities, was constructed.
Abe, Hitoshi; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(1), p.10 - 21, 2007/03
In MOX fuel fabrication facility, zinc stearate will be added into the MOX powder as addition material. If the material is added in large excess by miss operation, criticality characteristics of the MOX fuel would be influenced because it has neutron moderation effect. If criticality condition should be induced by the excess addition, physical variations, such as melting and pyrolysis of the material, must be caused by the fission energy and dynamic characteristics of the MOX fuel must be affected. To contribute quantitative evaluation of the dynamic characteristics, thermal properties data such as exo/endothermic calorific values, reaction rates, etc. with the respective physical variations and release behavior of pyrolysis gas were measured. It was found the exo/endothermic behavior with rinsing temperature of the material could be divided into six regions and rapid pressure rise caused by the pyrolysis reaction over about 400  C. Furthermore, on the basis of the results, evaluation model for the thermal properties under the criticality condition was also investigated.
C. Furthermore, on the basis of the results, evaluation model for the thermal properties under the criticality condition was also investigated.
Asahi, Yoshiro; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nakatsuka, Toru
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 152(2), p.219 - 235, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)An analysis of a BWR turbine trip experiment was performed with the THYDE-NEU code. The plant was treated as a closed coolant system whose pressure ranges to the atmospheric pressure. To simulate an entire plant, it was found necessary to have the moisture separator model and to account for reversible pressure drops at a junction with an area change. A spatial kinetics model without a notion of reactivity was applied. It was confirmed that THYDE-NEU can perform a coupled neutronic and thermal-hydraulic null transient at the hot full power. Among factors influencing spatial kinetics in the turbine trip were the temporal behavior of the bypass valve opening, the thermal non-equilibrium model and the manner in which to express the coolant density used in the table look-up of cross sections. By adjusting these factors, it was found possible to generate the scram signal when the core averaged LPRM output reached the prescribed value. The other calculated results also were found satisfactorily in agreement with the experimental results.
Asahi, Yoshiro
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-002, 332 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
; ; Yamazaki, Toshihiko; ; ; Kondo, Toshinari*; *
JNC TN8400 2001-030, 99 Pages, 2002/01
There is a great deal of that we build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground. In an atomic energy institution, a study request is strong. When we build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground, evaluation of earthquake vibration of a vertical direction is an important problem. In an atomic energy institution, we design it by big earthquake load, and therefore examination is necessary. And, in this study, we do examination to build a Base-Isolated building with the quaternary deposit ground, we report it about an evaluation method of a design. Furthermore, we report that we estimated pipe laying and machinery to put in a building of Base-lsolated.
Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Hayashi, Kazuhiko; Motohashi, Jun; Kawashima, Kazuhito; Ichimura, Toshiyuki; Tamai, Kazuo; Takeuchi, Mitsuo
JAERI-Tech 2001-084, 110 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Murayama, Yoji
JAERI-Tech 2001-072, 58 Pages, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Asahi, Yoshiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Ose, Yasuo*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 139(1), p.78 - 95, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Obara, Toru*; Nakajima, Ken; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Sekimoto, Hiroshi*
JAERI-Research 2001-037, 60 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Ken
JAERI-Research 2001-003, 29 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
JAERI Task Force for Supporting the Investigation of JCO Criticality Accident
JAERI-Tech 2000-074, 216 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Wada, Shigeru; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Kazuhiko; Murayama, Yoji
JAERI-Tech 2000-054, 51 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English